Google’s latest advancements in on-device artificial intelligence represent a significant leap forward in personal communication technology. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on cloud processing, these innovations empower devices to deliver swift, private, and highly nuanced features directly on the hardware. One standout development is the enhancement of real-time translation during phone calls, which now incorporates voice synthesis that mimics the speaker’s natural tonality. This breakthrough means that when engaging in multilingual conversations, the translated speech doesn’t just sound robotic or generic—it approximates the speaker’s voice, adding an unprecedented layer of authenticity and emotional context.
This technology is not yet perfect; there are subtle imperfections in pronunciation and accent transfer, but the overall realism is striking. Imagine a business executive negotiating in Japanese or a family reconnecting across languages, all with the feeling of having a face-to-face conversation. The AI’s ability to preserve tone, pitch, and even subtle emotional cues makes these interactions feel more genuine. Moreover, all processing occurs locally on the device, assuring privacy and eliminating delays caused by network latency. As more languages are added and the system is refined, this capability could redefine how we bridge language barriers on a personal and professional level.
Privacy and Ethics in the Era of Voice Cloning
A highly innovative aspect of Google’s new voice translation feature is its capacity to generate a near-accurate clone of a speaker’s voice to deliver translations. During a demo, a Google employee illustrated how the assistant produces an artificial voice resembling the original speaker, which then recites the translated speech. This creates a seamless experience, making the translation feel natural and less disjointed.
However, this technology raises profound privacy and ethical questions. The notion that voice can be synthesized to sound like an individual—even with assurances that no audio data is stored or recorded—inevitably prompts concerns about misuse. Could such technology be exploited to impersonate someone maliciously? Are users fully aware of the nuances of voice cloning? Google claims to prioritize user privacy by ensuring on-device processing and not storing audio data, but the broader societal implications demand careful scrutiny. Ethical deployment, transparent policies, and robust security measures are essential if such powerful tools are to be harnessed responsibly.
Smart Personal Journaling and Daily Planning Innovations
Beyond communication, Google is venturing into personal well-being and productivity optimization through its new Google Journal app. Drawing inspiration from competitors like Apple, Google’s take emphasizes guided reflection, where prompts help users explore their emotions and experiences. The integration of AI-powered insights and sentiment tagging with emojis fosters an intuitive way to track mental health over time, offering users meaningful feedback about their mood patterns and overall well-being.
This development aligns with a broader trend towards using AI not just as a tool, but as a personal coach. The app’s customizable prompts and reflections tap into a desire for deeper self-awareness, blending technology with mental health support. Lockable behind a passcode, the journal provides a safe space for candid expression, which is crucial in maintaining user trust. While some may worry about data privacy, Google’s emphasis on local processing and encryption assures users that their introspective journeys remain confidential.
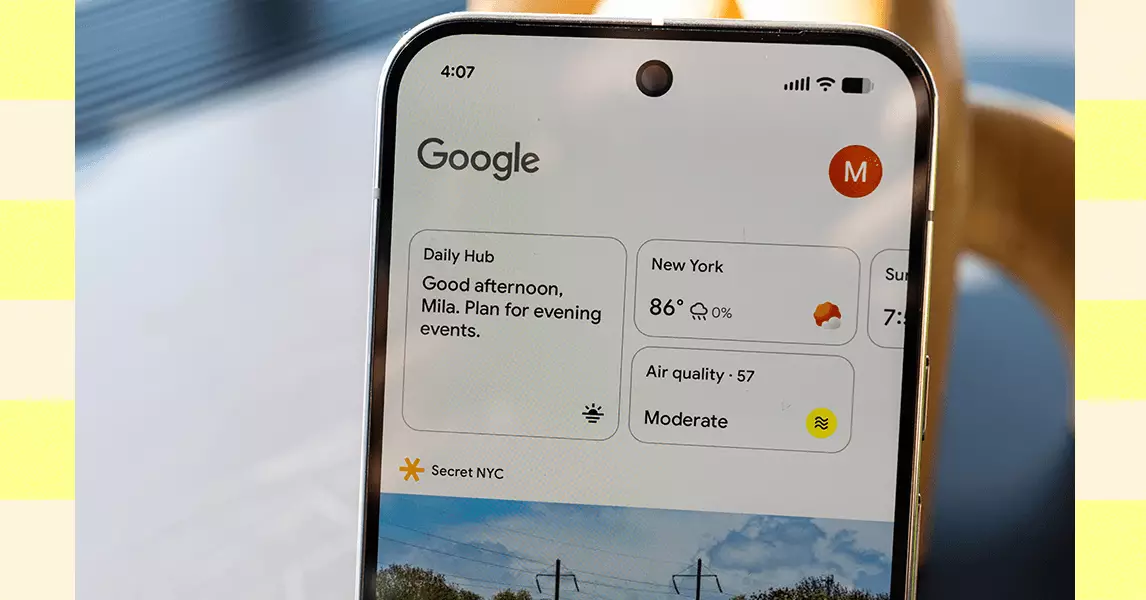
Enhancing Daily Routines with Subtle, Smart Interventions
Similarly, Google’s Daily Hub feature exemplifies the shift towards subtle, intelligent assistants that weave into daily life without overwhelming the user. Unlike more intrusive notification systems, this feature discreetly appears in minimal interfaces like the At a Glance widget or Google Discover. It offers essential information—such as calendar reminders, personalized activity suggestions, and upcoming events—without disrupting the flow of the day.
The seamless activation of Google Gemini on wearable devices, like the Pixel Watch 4, exemplifies this philosophy. Users can simply raise their wrist, and the assistant springs to life without voice commands or buttons. The AI’s improved understanding of natural language means users can converse more casually, whether to ask about last email summaries or to get dining suggestions. These features reflect a fundamental shift toward more intuitive, human-like interactions with technology, fostering a sense of partnership rather than invasion.
While still in its nascent stages, Google’s latest AI innovations lay the foundation for a future where devices are smarter, more private, and astonishingly human in their interactions. Their ability to deliver authentic voice translation, personalized journaling, and unobtrusive daily assistance showcases a clear trajectory towards deeply integrated AI that empowers users without compromising privacy. Yet, with these advances come significant responsibilities—ethical considerations around voice cloning and data security must be addressed with equal vigor. If managed thoughtfully, these innovations possess the transformative potential to redefine personal communication and daily life, turning smartphones and wearables from basic tools into empathetic, intuitive companions.