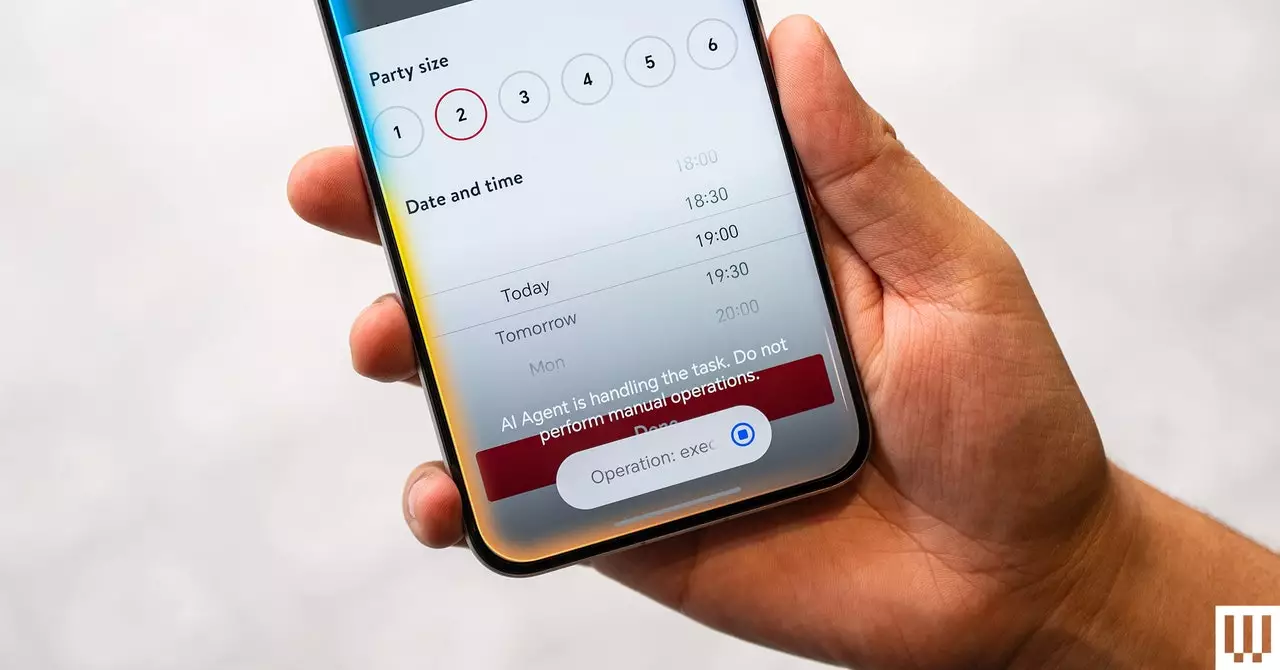
In an age where convenience reigns supreme, the advent of AI-driven personal assistants has revolutionized how we interact with technology, especially in the realm of dining reservations. However, a significant challenge persists: the hurdles encountered during the reservation process itself. For instance, when an AI assistant selects a restaurant, it may culminate in a situation where the user is stalled due to requirements such as a credit card for reservation confirmation. These scenarios highlight the limitations of current technology; while AI can efficiently identify options based on user preferences, it often falls short of completing tasks autonomously, leaving users to navigate inherent complexities.
Artificial Intelligence has made remarkable strides in understanding user intent, particularly when users express a desire for “highly rated” dining establishments. The AI processes available reviews and aggregate ratings, aiming to align with user expectations. However, the approach lacks depth; it does not cross-reference databases or delve into reviews beyond initial scores, operating solely within its local capabilities. This limitation emphasizes the need for more holistic AI systems that integrate diverse data sources to enhance decision-making processes. When AI relies on static, localized information, it risks providing recommendations that may not align with evolving consumer preferences or market trends.
The tech ecosystem buzzes with excitement over “agentic” AI, a term that signifies a new frontier in artificial intelligence competence—systems that can perform tasks on behalf of users with minimal supervision. A notable advancement came from Google’s Gemini 2 AI model, which aims to execute actions autonomously within user-defined parameters. This development marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of generative user interfaces, especially in mobile technology. At events like MWC 2024, the industry showcased innovative concepts whereby AI assistants generate interfaces dynamically, responding to verbal commands and fostering a fluid interactive experience devoid of conventional app navigation.
One intriguing approach is reminiscent of the Teach Mode featured in the Rabbit R1, where users can manually train an AI assistant to perform specific tasks. This method eliminates the reliance on traditional API connectivity, a common barrier that often hampers app interactions. Instead, the AI learner can adapt through memorized processes that grow more sophisticated over time. This evolution towards adaptable assistance signifies an exciting paradigm shift where users might ultimately train their digital helpers, transforming the way we interact with technology and each other.
The future of AI-driven personal assistants holds promise but also challenges. Developers must prioritize a user-centric approach, enhancing the autonomy and flexibility of AI capabilities while ensuring seamless interactions. As technology progresses, the goal should be to create intelligent systems that not only execute tasks but also evolve with users’ preferences, thereby simplifying everyday activities like dining reservations. This vision will pave the way for a new standard in personal assistance, where technology anticipates needs with precision, making complicated processes feel effortless and intuitive.